Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Welcome, fellow readers, to another exciting journey into the world of metallurgy and mining! Today, we’ll delve into the how bronze is mined (or rather produced), uncovering its step-by-step process, exploring the techniques used during the Bronze Age, and highlighting the impact it has had on ancient civilizations and our modern world. So grab your mining helmets and let’s dive in!
At the heart of bronze lies the art of mining, but is might not be what you think…
To make bronze miners need to first mine some copper and tin, the process is very long but interesting.
Let’s walk through the key steps involved in mining the ores to make this remarkable alloy.
Before the pickaxes hit the ground, extensive exploration is carried out to identify potential copper and tin deposits; the ores needed to make bronze.
Geologists and mining experts scour the Earth, studying rock formations, conducting surveys, and analyzing geological data to pinpoint promising sites.
For this you might want to get the help of a geologist that specializes in copper mining.
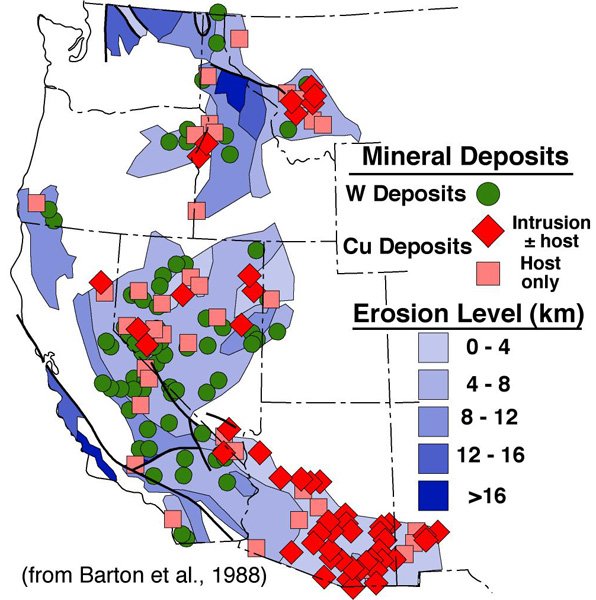
However, if you want to get a heads up about the best zones in America for copper and tin mining you can use this interactive mining map.
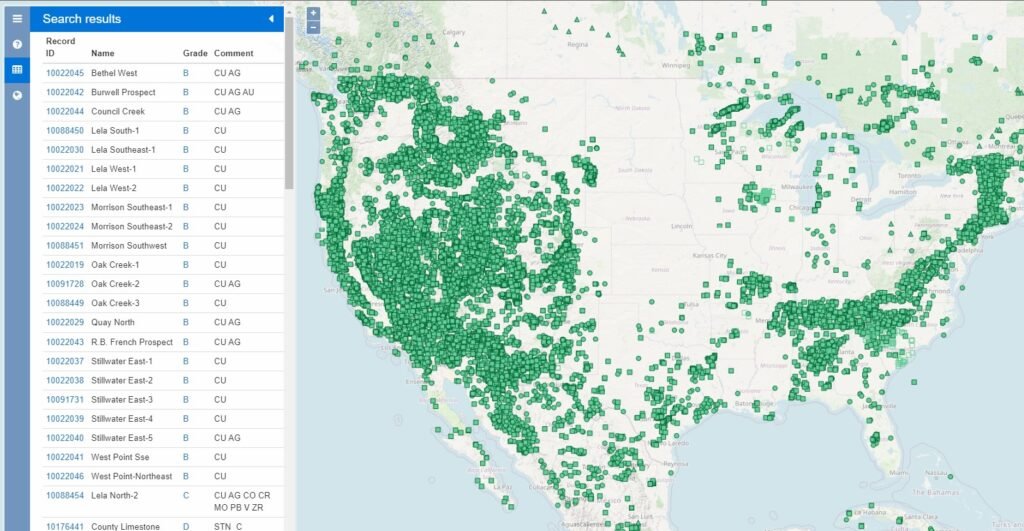
As you can see in the picture above we have filtered the mine so it shows us all the relevant copper mines registered.
So with this absolutely valuable information in hand you can start to get a notion of where copper can be found in America, Canada and even Mexico!
A thorough geological survey is critical for a successful mining operation. Geologists examine the composition of rocks and identify ore-rich areas that contain the primary minerals required for bronze production: copper and tin.
Miners look for areas with lots of green or blue-green minerals on the surface. These minerals often indicate the presence of copper ores below.
Here’s an example of what the ground looks like for us to find some copper and/or tin:
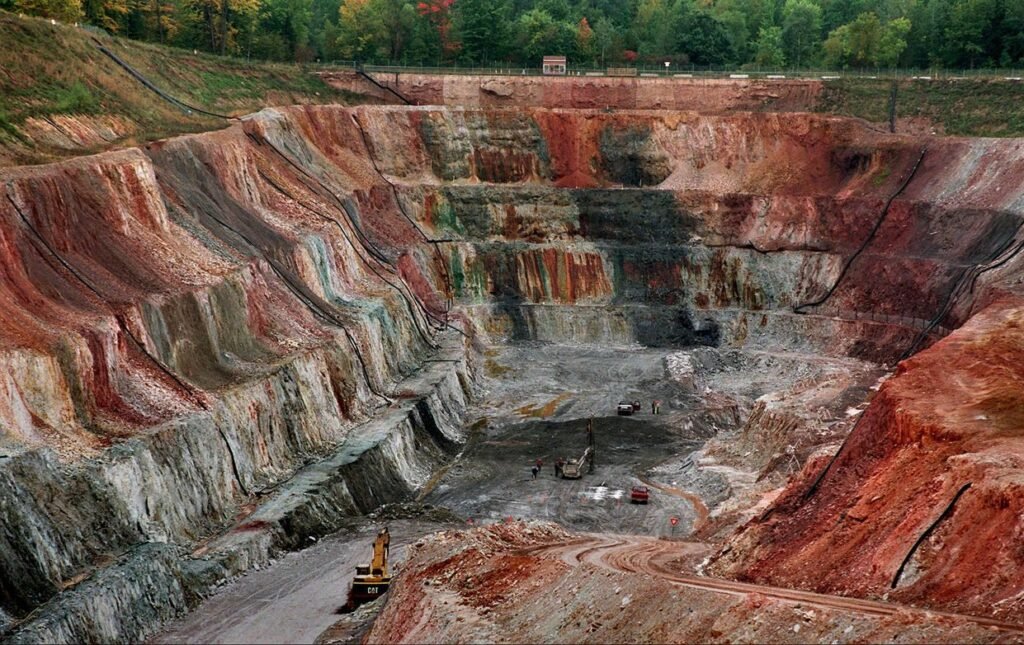

In this image we can appreciate how the ground in the open pit copper mine is colored, as you see most of it red-reddish and there’s also a lot of green colored ground which indicates the presence of copper ore.
Once a potential deposit is identified, meticulous planning and design take place. Mining engineers work to determine the most efficient and sustainable methods of extraction, considering factors such as access, safety, and environmental impact.
There are various techniques used to extract bronze from the ground. Surface mining, which involves removing layers of soil and rock to access the ore, is commonly employed when the deposit is near the surface.
Open-Pit Mining: Most copper is mined using big open pits. Massive machines dig into the Earth, removing layers upon layers of rock to expose the copper ores.
Underground mining: This type of mining on the other hand, is utilized for deeper deposits and involves creating tunnels and shafts to access the ore. Underground mining is often utilized to extract tin ore.
After extraction, the ores undergo a series of processes to refine and prepare them for bronze production.
This typically involves crushing the ores into smaller pieces, followed by grinding and chemical treatments to separate the copper and tin minerals from impurities.
Getting Smaller: Once the ore is extracted, it needs to be broken down into tiny pieces. Machines crush the hard rock into a fine powder, making it easier to extract the copper and tin.
This is where science feels like magic. The crushed ore is mixed with water and chemicals, then aerated (think bubbly!).
The copper particles attach to the bubbles and float to the top. The gunk we don’t want sinks. We then scoop off the copper-rich froth from the top.
This explanation might be a little confusion we know, so here’s a picture that shows the equipment needed for the flotation process as well as showing how flotation works step by step:
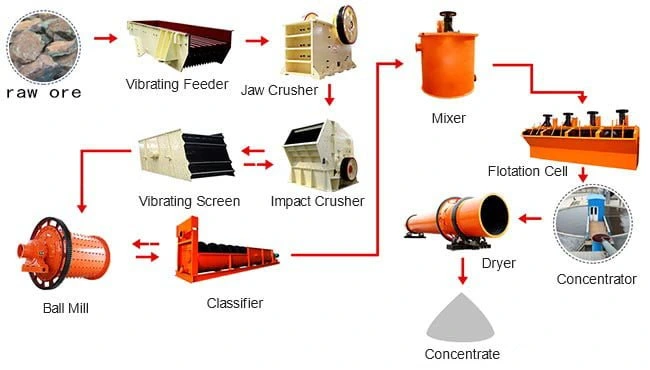
If you’ve ever played Minecraft you’ll be familiar with this process: The ore concentrate from the flotation process is then heated super hot.
This process separates the metal from other elements, giving us nearly pure copper and tin.
We’ll leave with with a really interesting video that shows the whole mining process of copper and tin as well as smelting these two ores, skip to minute 1:21.
Alloying: Finally, the fun part! Copper and tin are melted together in specific ratios (typically around 90% copper and 10% tin, though this can vary).
Here’s a video of the process:
When they cool and solidify, voilà! We have bronze.
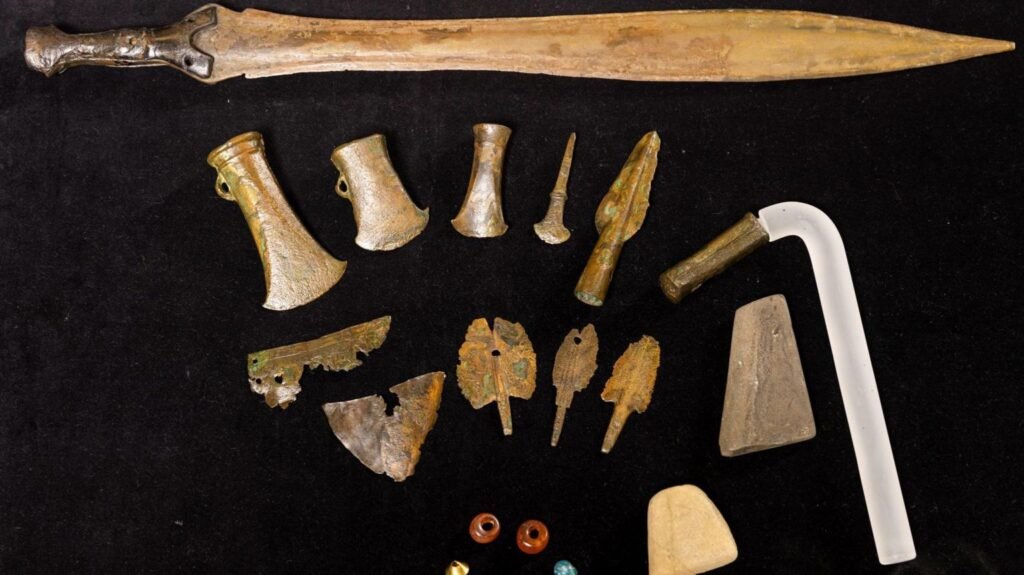

Let’s take a leap back in time to the Bronze Age, where mining techniques were rooted in ingenuity and resourcefulness.
During the Bronze Age, surface mining played a crucial role in extracting the ores needed for bronze production.
Miners would manually dig pits or trenches to access the ore-rich layers of the Earth. As mining operations expanded, underground mining techniques were introduced, involving the creation of simple tunnels and galleries.
The tools used during the Bronze Age were relatively basic but effective. Miners employed stone hammers, picks, and chisels to extract the ores, while baskets and simple carts aided in transportation. These ancient miners truly embodied the spirit of perseverance and innovation.
Bronze production flourished in various regions during ancient times, each leaving its unique mark on history.
The ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, Indus Valley, and China were renowned for their bronze craftsmanship.
Fast forward to modern times, and bronze production is a global affair. Countries like China, Russia, Chile, Peru, and the United States are among the top producers of bronze today.
The widespread use of bronze in industries such as construction, automotive, and art has fueled its demand worldwide.
This is an example of an open pit mine in Sweeden: Aitik. Aitik is primarily known for its copper production.
Bronze is an alloy made mainly of copper, typically combined with tin and sometimes other metals like zinc.
While Aitik does not produce bronze directly, its relevance in bronze production lies in its contribution of one of the primary ingredients: copper.
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the mining industry, making bronze mining more efficient, safe, and environmentally conscious.
Today, sophisticated machinery and equipment, such as drills, excavators, and haul trucks, have replaced much of the manual labor involved in mining.
These powerful tools increase productivity while ensuring the safety of miners. Modern mining operations also employ state-of-the-art monitoring systems to detect potential hazards and maintain optimal working conditions.
Let’s compare the mining techniques of ancient civilizations with those employed in the modern era:
| Aspect | Ancient Mining Methods | Modern Mining Methods |
| Equipment | Basic tools, stone hammers | Advanced machinery and technology |
| Extraction Efficiency | Limited | High |
| Safety | Higher risks | Stringent safety protocols |
| Environmental Impact | Less regulated | Strict environmental standards |
| Productivity | Relatively low | Significantly higher |
Ancient civilizations relied on their resourcefulness and sheer determination to extract bronze ores. While their methods were less efficient and more hazardous, they paved the way for the development of modern mining techniques.
To create bronze, copper and tin, the primary ores, are combined through a process called smelting. Here’s a simplified overview of the production process:
That is a simple but accurate summary on how is bronze mined using modern techniques and equipment. Today bronze production is relatively simple and safe to carry out.

The primary ores used for bronze production are copper ore and tin ore. Copper ore typically contains copper sulfide minerals, such as chalcopyrite, while tin ore consists of tin oxide minerals, such as cassiterite.
Copper ores are widely found across the globe, with major deposits in countries like Chile, Peru, and the United States. Tin ores are rarer, with significant deposits located in countries such as China, Indonesia, and Bolivia.
Several bronze mines and archaeological sites bear witness to the rich history of bronze mining. Some notable examples include:
In the production of bronze, the smelting process brings together copper and tin ores. Through ore preparation, smelting, and alloying, the molten bronze is created, ready to be shaped into various forms for different applications.
The primary ores used in bronze production are copper ore, rich in copper sulfide minerals, and tin ore, containing tin oxide minerals. These ores are found in various regions worldwide, with significant deposits contributing to global bronze production.
Bronze mines and archaeological sites offer glimpses into the ancient world of mining. Sites like the Great Orme Bronze Age Mine, the Faynan Copper Mines, and Mount Gabriel serve as a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient miners.
The comparison between ancient and modern mining methods highlights the progress we have made in terms of safety, productivity, and environmental consciousness. While ancient civilizations relied on basic tools and took on higher risks, modern mining practices prioritize the safety of workers and the preservation of the environment.
While the extraction of valuable minerals is essential, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact of mining activities.
Bronze mining, like any other mining process, can have environmental consequences. Excavation and the use of heavy machinery can disrupt ecosystems, alter landscapes, and potentially lead to habitat destruction.
Additionally, the release of mining byproducts and tailings into water sources can impact water quality and aquatic life.
To mitigate these effects, modern mining industries implement strict regulations and environmental management practices. These include proper waste management, reclamation of mining areas,
reclamation of mining areas, and the use of advanced technologies to minimize pollution and resource consumption.
Sustainable mining practices aim to strike a balance between resource extraction and environmental preservation.
Bronze mining has played a pivotal role in human history, shaping civilizations and enabling technological advancements. From the Bronze Age to modern times, the journey of extracting bronze from the earth has evolved significantly.
Ancient mining techniques, driven by human ingenuity, laid the foundation for the advanced mining methods we employ today. As we delve deeper into the secrets of bronze mining and how is bronze mined, we must also strive to minimize its environmental impact through sustainable mining techniques.
Modern bronze mining combines technological advancements, stringent safety measures, and environmental regulations. So how is bronze mined? From exploration and site identification to the extraction and processing of ores, every step is carefully planned and executed. We have witnessed a remarkable shift from manual labor to the use of powerful machinery, increasing efficiency and productivity while ensuring the well-being of miners.
Bronze is not mined directly as it is an alloy composed primarily of copper and tin. The mining process involves extracting these base metals, which are then combined to create bronze. To understand how other metals are mined or produced, explore the following resources:
If you also want to learn more about some other less common metals, their uses, history, facts and much more here we have some other honorable mentions worth checking out:
By exploring these different metals and their mining or production processes, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how bronze is created from its base components and how these methods compare to the unique processes of other essential materials.
As we conclude our journey into the secrets of bronze mining, let us appreciate the profound impact this alloy has had on human history. Bronze has shaped our world, from tools and weaponry in ancient times to architectural marvels and artistic creations today. It is a testament to human innovation and the eternal quest for progress.